
DIO, also known as DSI (days sales of inventory), is calculated based on the cost of goods sold (COGS), or acquiring or manufacturing the products. For potential investors and lenders, understanding a company’s APP can reveal important insights into the firm’s cash flow management, financial sustainability, and overall risk profile. Investors prefer companies that demonstrate financial discipline and efficient cash management, for which the APP serves as a significant indicator. Inventory holding period This is calculated in a very similar way to the receivables collection period. Again, for liquidity purposes the shorter this period the better, as less cash is tied up in inventory.
Ready to transform your AP?
Generally, the higher the better, but in later studies you will consider the problems caused by overtrading (operating a business at a level not sustainable by its capital employed). Commonly a high asset turnover is accompanied with a low return on sales and vice versa. Therefore, the A/P days metric tracks the number of days it takes for a company to fulfill its obligation to pay its outstanding invoices owed to suppliers or vendors. A/P Days counts the average number of days it takes for a company to fulfill an invoice from suppliers or vendors for orders placed using credit.
Formula for Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)
Beyond the monetary value involved, CCC accounts for the time involved in these processes and provides another view of the company’s operating efficiency. By showcasing the diverse effects on various sectors, these case studies will provide a holistic view of how the average payment period can directly influence business success. With the current ratio it is not the case of the higher the better, as simple invoices in 9 steps a very high current ratio is not necessarily good. Cash is often described as an ’idle asset‘ because it earns no return and carrying too much cash is considered wasteful. A high ratio could also indicate that the company is not making sufficient use of cheap short-term finance. In the next section of our exercise, we’ll forecast our company’s accounts payable balance for the next five periods.
Average Payment Period Calculation Example
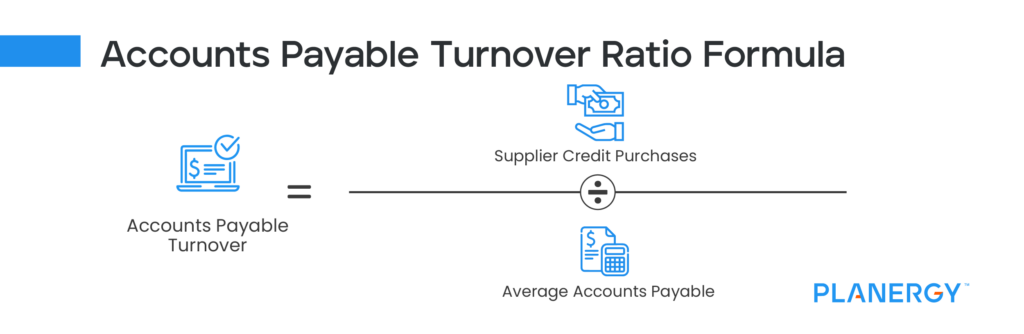
A higher DPO value means the company holds onto cash longer, thus increasing its investment potential. Conversely, a lower accounts payable turnover ratio usually signifies that a company is slow in paying its suppliers. The ratio is calculated on a quarterly or on an annual basis, and it indicates how well the company’s cash outflows are being managed. Accounts payable turnover is a ratio that measures the speed with which a company pays its suppliers.
- This result means the company, on average, takes around 61 days to pay its suppliers.
- Therefore, a good average payment period will depend on things like a huge volume of order, orders are placed very frequently and the customer and supplier have good relation with each other.
- A higher DPO value means the company holds onto cash longer, thus increasing its investment potential.
- Similar companies should produce similar financial metrics, so the average collection period can be used as a benchmark against another company’s performance.
Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. However, the ending A/P balance is often acceptable in practice, as the insights derived will rarely be that different under either approach, barring unusual circumstances.
Accounts payable are short-term liabilities relating to the purchases of goods and services incurred by a business. The days payable outstanding (DPO) ratio, which measures a company’s solvency, measures how long it takes a company to pay its short-term liabilities, particularly for purchases it makes on credit. An essential financial metric for companies to assess how well they settle their debts quickly is the average payment period.
Speaking of improving your relationship with your supplier, learn more about how to strengthen it with effective strategies, especially for international trade. The ideal Days Payable Outstanding depends on your business needs and industry benchmarks, with no universal standard. The relationship between DSO and DPO can indicate the balance between inflows and outflows of cash.
The state of the business’s accounts receivable and outstanding customer payments, which are essential elements of its revenue, are not taken into account by this metric. For instance, a company’s accounts receivable balance might indicate that clients have finished a purchase but not yet finished the payment cycle, deferring actual payment to a later time. However, the APP doesn’t consider this potential cash flow when determining whether or not the company can afford to pay its debts. The second stage focuses on how long the company takes the company to collect the cash generated from sales. This figure is calculated using the days sales outstanding (DSO), which divides average accounts receivable by revenue per day.
